Umbilical Cord Blood
Stem Cell
Umbilical Cord blood, also known as hematopoietic stem cells (blood-forming stem cells), possesses similar properties to stem cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood but is younger and more easily developed into other cell types. The primary function of these cells is to generate new red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets to replace old, expired ones.
The blood in the placenta and umbilical cord of a newborn is a significant source of stem cells that can be collected immediately after birth for use in treating a wide variety of medical conditions. This may be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity for you as parents to preserve something invaluable as a gift for your newborn.
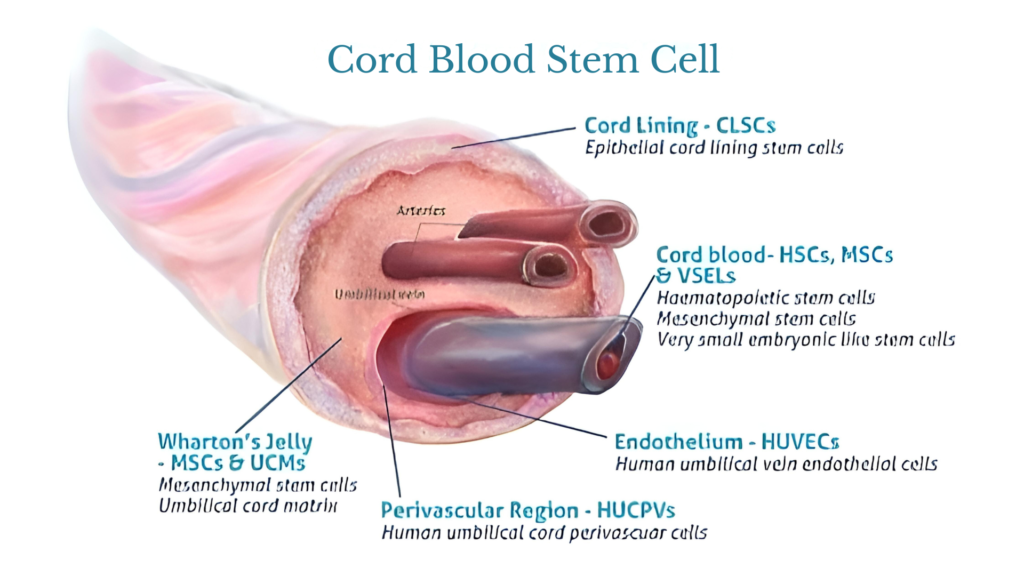
The blood in a newborn’s umbilical cord is one of the critical sources of adult stem cells, known as umbilical cord blood stem cells, that can be collected right after birth. Following collection using our internationally standardized closed system, the blood is sent to our laboratory in Bangkok (not to a distant lab prone to flooding or in rural areas) for processing using the latest SEPAX technology.
processed stem cells are then cryogenically frozen at -196 degrees Celsius, halting all cellular activities in the most optimal environment for stem cell preservation. Choose to store your child’s umbilical cord blood stem cells in Bangkok with Thai StemLife to avoid the risks associated with potential loss of cold chain integrity during international transport.
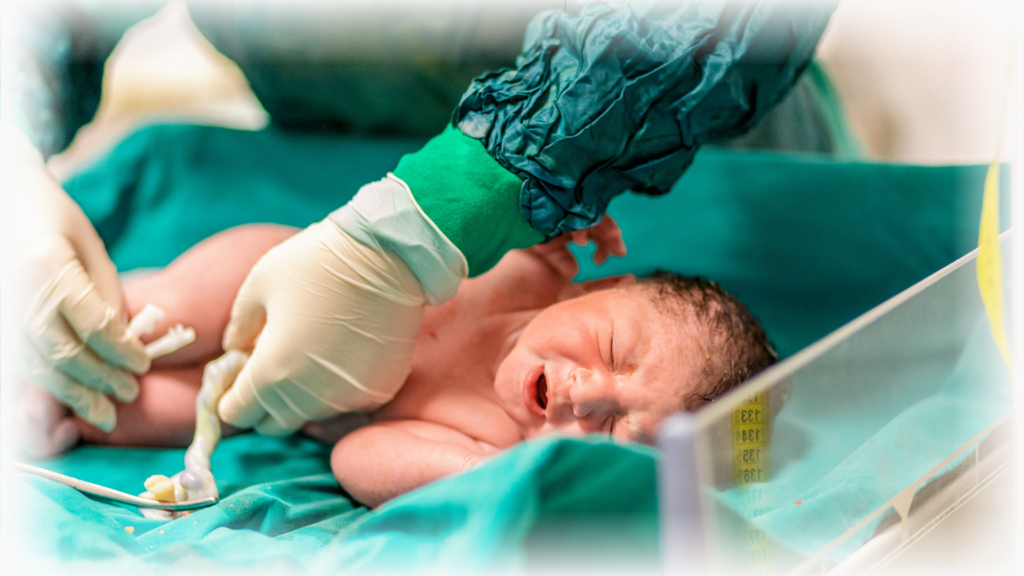
Umbilical cord blood collection is a simple procedure that can be done immediately after your baby is born, without any risk or disruption to the normal birthing process (whether vaginal delivery or cesarean section). Within just 5 minutes, the cord blood can be collected after the obstetrician cuts the umbilical cord, with no pain or discomfort to either the mother or baby!
The chance of tissue matching within the same family is significantly higher than with unrelated individuals (1 in 4 compared to 1 in 50,000), meaning other family members may potentially benefit from stored stem cells if needed in the future (tissue compatibility with HLA testing required). In the future, the indications for stem cell use are expected to increase.
Currently, more than 100 diseases can be treated with stem cells, with rapidly growing applications. These may include potential future treatments for cardiovascular or neurological conditions (e.g., stroke, spinal cord injury). Research studies for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases are showing promising results. Globally, the number of families opting to store valuable stem cell-rich cord blood is increasing, and this service is available to you as well.

2. Congenital metabolic disorders:
-
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) (e.g., Hunter or Hurler syndrome)
- Leukodystrophies
- Glycoprotein storage diseases (e.g., fucosidosis, mannosidosis)
- Lysosomal storage disorders (e.g., Gaucher disease, Pompe disease, Niemann-Pick disease)
- Osteopetrosis (marble bone disease)
- Collagen-related congenital bone diseases
3. Hemoglobinopathies:
-
- Thalassemia
- Sickle cell anemia
Diseases treatable by stem cell transplants include:
1. Immune system disorders:
-
- Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Bone marrow failure syndromes:
- Severe aplastic anemia
- Fanconi anemia
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia


4. Cancers or blood disorders originating from bone marrow:
-
- Acute leukemia
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
- Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
- Bone marrow disorders with abnormal blood cell production, at risk of evolving into leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
5. Solid tumors:
-
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Testicular cancer
- Small cell lung cancer
- Ewing’s sarcoma in children
- Pancreatic cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Medulloblastoma (brain tumor)


6. Pediatric cancers:
-
- Wilms tumor (kidney cancer in children)
- Neuroblastoma
- Ewing’s sarcoma
- High-grade gliomas (e.g., medulloblastoma)
- Brain tumors
7. Other conditions:
-
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
- Acquired aplastic anemia
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., Type 1 diabetes)

